Is Rapid Prototyping the same as 3D printing?
The terms “rapid prototyping” and “3D printing” are often used interchangeably, but they actually represent two different processes. Understanding the difference between the two is important for choosing the right process for your needs.
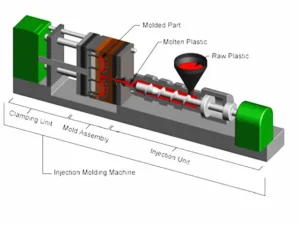
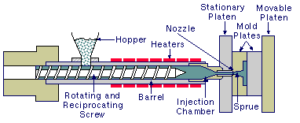
Rapid prototyping is the process of quickly creating a physical model of an object, typically for the purpose of testing and evaluating a product design. The process can use a variety of techniques, including 3D printing, CNC milling, and stereolithography.
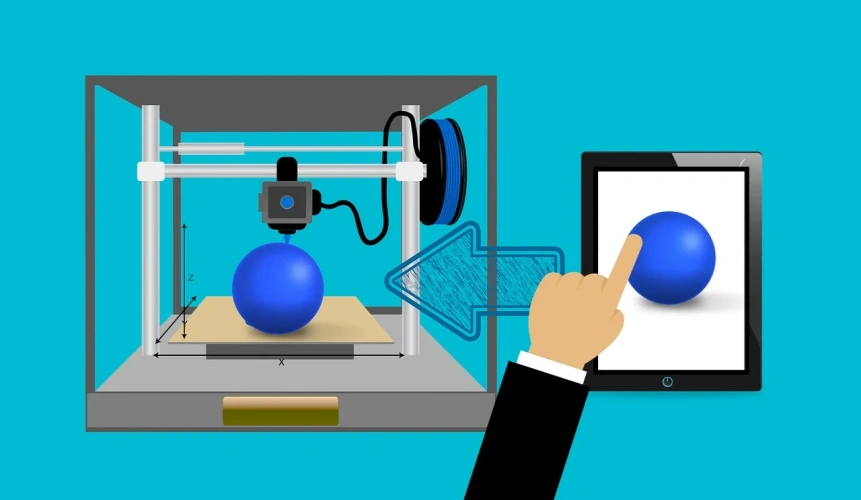
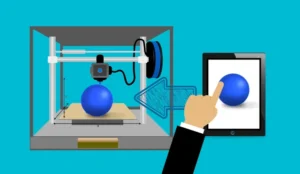
3D printing is a specific rapid prototyping technique that builds a three-dimensional object by depositing material layer by layer. 3D printers use digital files (usually CAD models) as instructions to create physical objects with a high degree of precision.
While 3D printing is one of the most common rapid prototyping techniques, it is not the only option. Other methods may be better suited for certain applications, such as:
- CNC milling is a good choice for parts that require high precision and surface finish.
- Stereolithography can be used to create parts with complex geometries.
Advantages of 3D printing
3D printing offers several advantages for rapid prototyping, including:
- Speed and efficiency: 3D printing can create prototypes much faster than traditional methods.
- Design freedom: 3D printing can be used to create parts with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Iterative: 3D printing makes it easy to iterate on designs and make changes without increasing costs.
- Customization: 3D printing can be used to create custom products and prototypes.
Applications of 3D printing
3D printing is used in a wide variety of industries, including:
- Automotive: 3D printing is used to create car parts, prototypes, and concept cars.
- Aerospace: 3D printing is used to create aircraft parts, satellite components, and rocket parts.
- Medical: 3D printing is used to create implants, surgical models, and custom medical devices.
- Consumer products: 3D printing is used to create products such as jewelry, glasses, and toys.
The future of 3D printing
3D printing technology is constantly evolving, and the range of its applications is expanding. As 3D printers become more affordable and easier to use, the technology has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping and 3D printing are both powerful tools for creating physical models. However, 3D printing offers several significant advantages in terms of speed, efficiency, design freedom, iteration, and customization. As 3D printing technology continues to develop, its applications will continue to expand, and it has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing.
Here are some specific examples of how 3D printing is superior to other rapid prototyping methods:
- A car company could use 3D printing to quickly create prototypes of a new car model. This would allow them to test and refine the design before going into mass production.
- An aerospace company could use 3D printing to create custom aircraft parts. This would allow them to reduce the weight of the aircraft and improve its performance.
- A medical company could use 3D printing to create custom implants. This would allow them to provide patients with a better fit and improved outcomes.
- A consumer product company could use 3D printing to create custom products. This would allow them to meet the needs of individual customers and provide a unique experience.
Overall, 3D printing is a powerful and versatile technology that can be used for a wide variety of applications. As the technology continues to develop, the impact of 3D printing is likely to grow even larger.