How Does Injection Molding Work?
An In-depth Look at the Plastic Manufacturing Process
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for creating high-quality plastic parts. It’s a versatile and cost-effective method for producing a wide range of products, from small components to large enclosures.
How Does Injection Molding Work?
The injection molding process involves several steps, each contributing to the creation of the final product:
1. Material Preparation
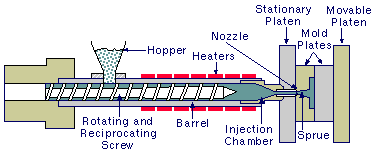
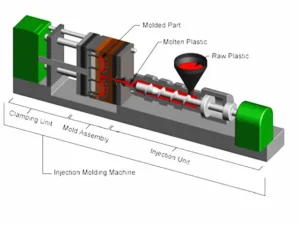
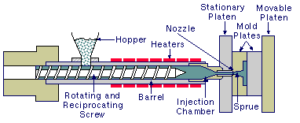
The process begins with the preparation of the plastic material, typically in the form of pellets or granules. These pellets are fed into a hopper, where they are heated and melted by a rotating screw. The screw also helps to mix and blend any additives or colorants that are required for the final product.
2. Injection and Molding
Once the plastic is molten, it is injected into a closed mold cavity under high pressure. The mold has been designed and manufactured specifically for the desired part shape. The pressure forces the molten plastic into every corner and crevice of the mold, ensuring that the part takes on the correct shape.
3. Cooling and Ejection
After the injection phase, the mold is cooled to allow the plastic to solidify. This cooling can be achieved using water jackets or circulating coolant around the mold. Exclamation Once the plastic has solidified sufficiently, the mold opens, and the part is ejected using ejector pins.
4. Trimming and Finishing
The ejected part may require some additional trimming or finishing processes to remove any sprues or runners, which are the channels through which the molten plastic was injected into the mold. The part may also be subjected to additional finishing processes, such as sanding, painting, or printing.
Factors Affecting Injection Molding
Several factors can influence the quality and success of the injection molding process:
Material Selection: The choice of plastic material is crucial for the part’s properties and performance. Factors such as strength, flexibility, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility must be considered.
Mold Design: The mold design plays a critical role in the quality of the final product. The mold must be able to withstand the injection pressure and ensure proper cooling and ejection of the part.
Injection Parameters: The injection parameters, such as injection pressure, injection speed, and cooling time, have a significant impact on the part’s properties. Careful optimization of these parameters is essential for consistent quality.
Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding is used in a wide range of industries, including:
Automotive: Plastic components for cars, trucks, and motorcycles, such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior trim panels.
Medical: Medical devices, such as syringes, catheters, and drug delivery systems.
Electronics: Electronic components, such as connectors, housings, and circuit boards.
Consumer Products: A vast array of consumer products, from toys and appliances to furniture and housewares.
Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding offers several advantages over other manufacturing processes:
High Production Rates: Injection molding can produce large quantities of parts quickly and efficiently.
Design Flexibility: Injection molding can create complex shapes and intricate details.
High-Quality Products: Injection molding can produce parts with consistent dimensions, high strength, and a smooth finish.
Cost-effectiveness: For high-volume production, injection molding can be a very cost-effective manufacturing method.
Conclusion
Injection molding is a versatile and powerful manufacturing process that plays a vital role in modern manufacturing. Its ability to produce high-quality plastic parts at high volumes makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. With its continuous advancements in technology and materials, injection molding is poised to remain a key manufacturing process for years to come.